This post is also available in:
 Deutsch
Deutsch
Traditional indicators for measuring research impact include the number of peer-reviewed publications (first / last / corresponding authorship) and h-index for researchers, or the impact factor for journals (JIF). However, these are difficults to compare between researchers, since they do not take into account the different publication and citation behaviours in different research areas. They also do not include when content is shared in online media, and they can only be calculated years after an article has been published. To overcome these shortcomings, new indicators such as Altmetrics or the Relative Citation Ratio have been proposed. None of these indicators, however, will tell you if this research has effects beyond academia and benefits society, culture or the economy.
Altmetrics
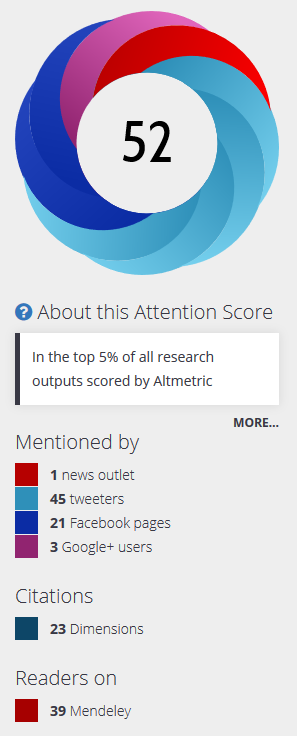
Altmetrics monitor whenever a research article is mentioned online (e.g. in blogs, Facebook, Twitter, Wikipedia, Reddit,…). The number of citations are counted, the sources are depicted in different colours in a doughnut, and an Altmetric Attention Score is calculated. Once you have installed the bookmarklet, you can get the Altmetric details for any article. Altmetrics are also displayed for articles in ZORA.
Plum X Metrics
Plum X Metrics work similarly by counting online activities in five categories: usage, captures, mentions, social media, and citations. Plum X Metrics is available on Scopus and other Elsevier products.
Relative Citation Ratio
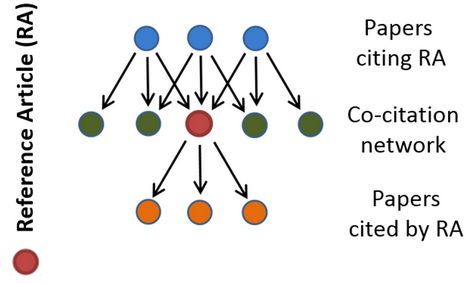
The Relative Citation Ratio (RCR) has been described in Hutchins et al. PLoS Biol. (2016) and critically discussed in Janssens et al. PLoS Biol. (2017). The RCR does not only look at how often a specific article (reference article, RA, see figure) has been cited, but also how often other articles that appear together with it in reference lists (“co-citation network”) have been cited. Thus, the average of all journal citation rates are defined as the RA’s field citation rate (FCR). The RCR is calculated by taking article citation rate to FCR ratio and adjusting it so that the average RCR equals 1.0 for any FCR. There is an online tool (iCite) for calculating RCRs, where you can e.g. have a look at the RCRs of your own papers.